| e-df.com | e-DataFunction Solutions | websites (navigation) |
| Previous page << | epi-1 epi-2 epi-3 | statistics epi-in Chinese | e-print |
|
Clicking >> ebook available |
PUBLIC HEALTH (Epidemiology)
>> World Health Organization (WHO) (WHO / Homepage) >> Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), USA >> Public Health Agency of Canada >> BC Centre for Disease Control (BC, Canada) |
![]()
| CDC's Illustrations | ||
|
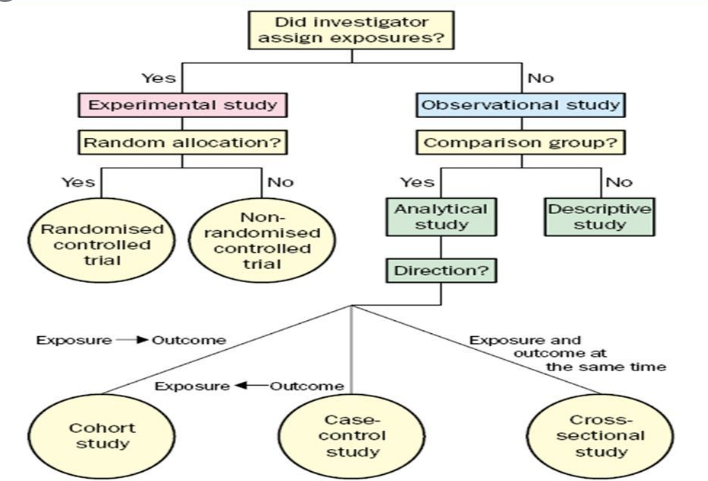
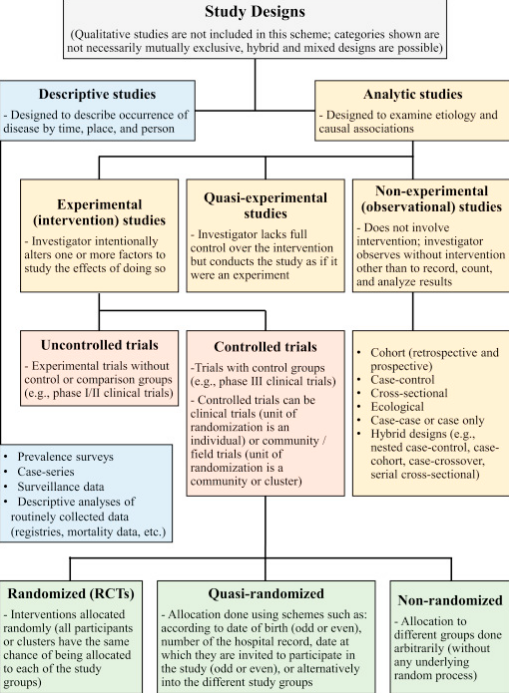
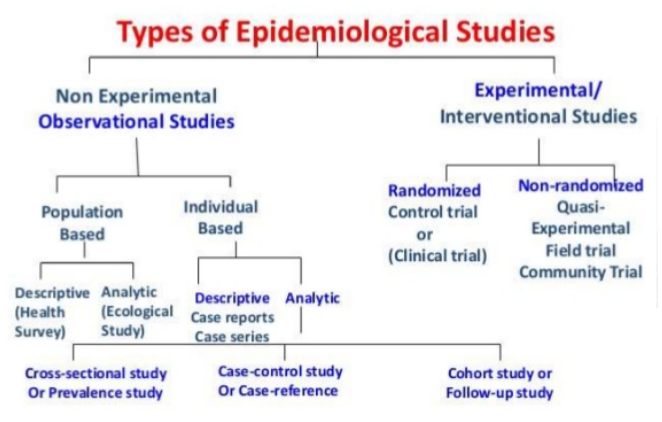
1. Descriptive
Where, When, and what (population) ; For the basic understandings 2. Analytical With the search for causes and effects, or the why and the how. Epidemiologists use analytic epidemiology to quantify the association between exposures and outcomes and to test hypotheses about causal relationships. Three methods: i) Case-control (indirect refection); ii) Cohort (direct hints); iii) cross-sectional (retrospective or prospective). 3. Experimental Experimental epidemiology is a type of epidemiological investigation that uses an experimental model to confirm a causal relationship suggested by observational studies. It studies the relationships of various factors determining the frequency and distribution of diseases in a community. 4. Theoretical Epidemiology: Knowing or understanding some factors in relation to diseases, establish the models for further trends or retesting the factors. (Paper Link)
Rate: Death rate / Mortality rate (crude death rate in a period, per 1K or 100K,in the same period, average population) Adjust death rate (directly or indirectly with age-group of population, indirectly usually with standards of national age-group per 100K) Morbility rate / Incidence rate (new case in period, per 1K, in the same period, exposure/average population) Attack rate (new case in short period or small scale, 100%, in the same period, exposure population) Prevalence rate (new and existing case in a period, per 1K or 100K, in the same period, average population, P=I*D, I-Incidence rate, D-During of illness) Secondary attack rate (SAR) (excluding the original case, 100%, in the same period, easy suffering from population) Fatality rate (death # from the case divided the total case #, or F=Mortality rate/Incidence rate; 100%) Infant death rate (yearly death/yearly survival, per 1K) Neonatal mortality rate (monthly death/yearly survival, per 1K) Introducing rate (i.e. family-group with sub-age-group of the case infected from outside, analysis of which age-group easy to bring the case to family) Excess mortality rate (i.e. comparing the pervious yearly M-rate of a Flu, monthly adjusted with the monthly M-rate of a new Flu.) Cumulative death rate (i.e. added all of age-group M-rate of all cancers to understand an age M-rate of cancers)
Sporadic; Epidemics; Pandemic; Outbreak. Endemic Imprted infectious disease
Sample size: S.E. (sample error) (y)=S.D./n^1/2 S.E. ={[I-rate * (1-I-rate)]/N}^1/2 If 0.1 allowed: N=400Q/P |
|
| WHO: International Classification of Diseases | ||
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
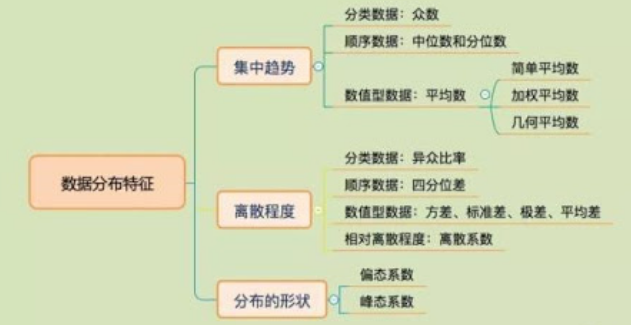
|
|
![]()
|
Epidemiology
>> International Journal of Epidemiology >> Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health >> Journal of Clinical Epidemiology Biostatistics>> Canada's national statistical agency |
Case Study
Future of Epidemiology |
|
|
omega369oil.com (nutrition) |
nose-care.com (nasal allergy & rhinitis) |
|
|
|
||
| Copyrights © by EDF Solutions Inc. All rights reserved. | Contact us / 联络 | About us / 关于我们 |